If you're choosing between 2.4GHz wireless keyboards and Bluetooth, here's the key takeaway: 2.4GHz wireless offers faster response times (1–3ms latency), higher polling rates (up to 8,000Hz), and more stable connections in crowded environments. It's perfect for gaming, coding, or tasks requiring instant feedback. Bluetooth, while slower (7–20ms latency) and capped at 125Hz polling, is more convenient for multi-device use and portability.
Key Points:
- Speed: 2.4GHz is faster than Bluetooth, making it ideal for gaming or fast typing.
- Stability: 2.4GHz handles interference better with private channels and frequency hopping.
- Battery Life: Bluetooth typically lasts longer, but 2.4GHz can drain faster at higher polling rates.
- Compatibility: Bluetooth works with multiple devices, while 2.4GHz relies on a specific USB dongle.
- Security: High-end 2.4GHz keyboards may offer AES encryption, but not all models are secure.
For the best of both worlds, consider tri-mode keyboards that combine USB-C wired, 2.4GHz, and Bluetooth options. This flexibility lets you switch between high-speed performance and convenience as needed.
How 2.4GHz Wireless Keyboards Work
The Basics of 2.4GHz Wireless Communication
Here’s the setup: your keyboard contains a tiny radio transmitter, while the USB dongle plugged into your computer serves as the receiver.
These devices communicate using the ISM band (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical), specifically between 2.400 GHz and 2.4835 GHz. This spectrum is unlicensed, meaning manufacturers don’t have to pay licensing fees to use it. It offers 14 channels, with channels 1, 6, and 11 being non-overlapping in the U.S..
Data is sent in small packets, and the communication is usually half-duplex - meaning the keyboard listens first, then transmits. To handle interference in crowded spaces, devices employ Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH). This technique identifies interference and shifts to less congested frequencies, ensuring a steady connection even when competing with Wi-Fi routers or microwaves.
On top of this, many keyboards use proprietary protocols to fine-tune performance.
Proprietary Protocols in Keyboards
Most wireless keyboards go beyond the standard 2.4GHz framework by implementing proprietary protocols tailored for speed. These custom systems strip out unnecessary data, focusing solely on keystroke information. The result? Latency as low as 1ms to 5ms, which is nearly indistinguishable from wired keyboards.
The downside is compatibility. These keyboards require the specific USB dongle designed by the manufacturer. But for users who care more about fast response times than universal compatibility, this dedicated connection delivers top-tier performance.
Keystroke Data Transmission
When you press a key, the keyboard sends an 8-byte report containing information like modifiers, reserved bytes, and up to six keycodes. The USB receiver communicates with your computer using Interrupt mode, which is built for low-latency data transfer. Your computer polls the receiver as often as every 1ms to check for new input.
Standard gaming keyboards operate at a 1,000Hz polling rate (sending one packet every 1ms). High-performance models push this further, achieving 4,000Hz (0.25ms) or even 8,000Hz (0.125ms). However, these higher rates come at a cost: faster battery drain. For instance, an 8,000Hz keyboard can consume 28–35 mA and last only 12–15 hours on a 500mAh battery, compared to 70–80 hours at 1,000Hz.
To reduce packet loss - especially in crowded environments - keep the USB dongle within 12–20 inches of your keyboard using a USB extension cable. Avoid plugging the dongle into rear I/O ports on metal PC cases, as the metal can block signals and internal components may create interference.
This combination of efficient data transmission and interference management ensures a reliable and responsive experience.
sbb-itb-3cb9615
Cut the Cord? Wired vs. Wireless vs. Bluetooth
2.4GHz vs. Bluetooth: Key Differences
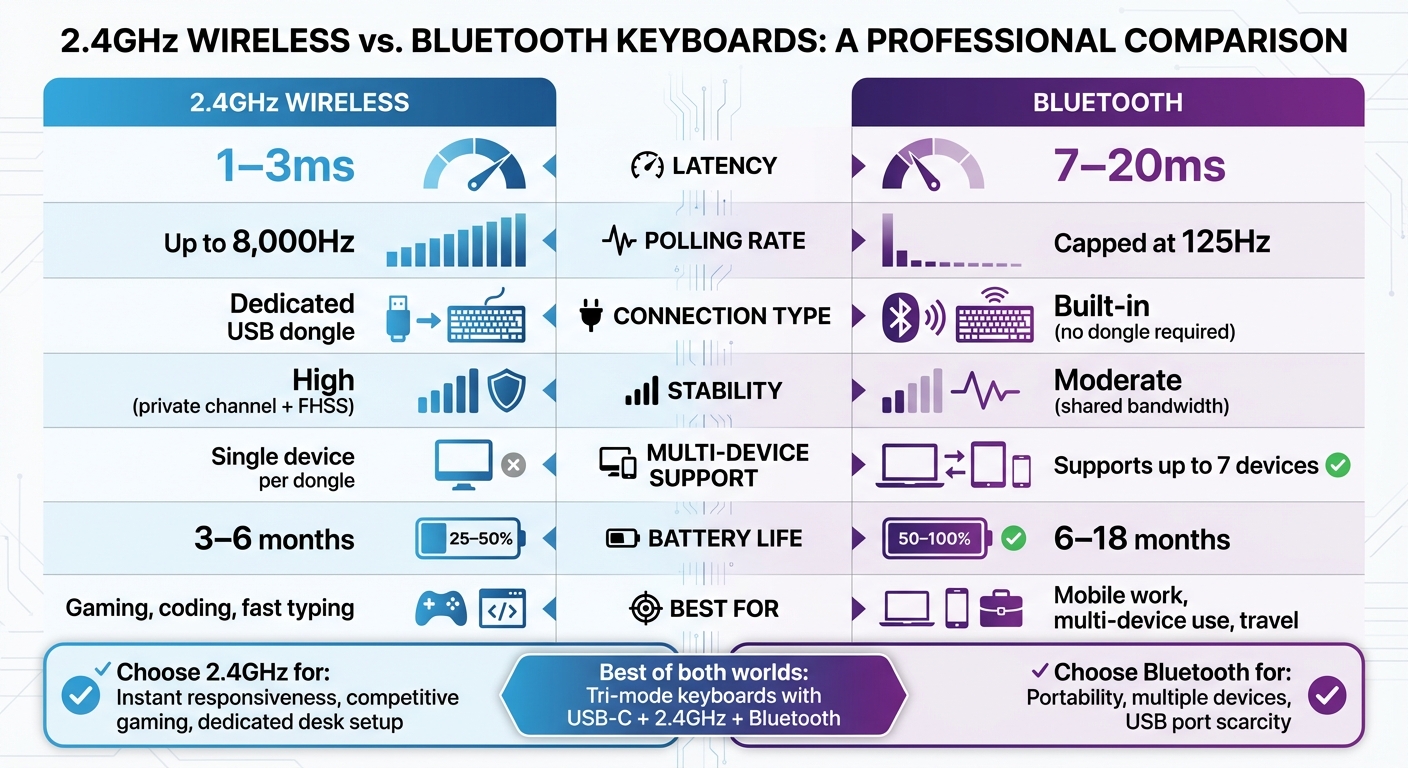
2.4GHz Wireless vs Bluetooth Keyboard Comparison Chart
Latency and Responsiveness
When it comes to latency, 2.4GHz wireless delivers an impressive 1–3ms, rivaling the performance of wired connections. On the other hand, Bluetooth operates with a latency of 7–20ms. This gap arises from their design priorities: 2.4GHz relies on a dedicated USB receiver, creating a private channel that minimizes data overhead. In contrast, Bluetooth prioritizes compatibility and energy efficiency, which inevitably adds processing delays.
The polling rate - the frequency at which the device communicates with the computer - also highlights this difference. Bluetooth is limited to 125Hz due to Human Interface Device (HID) specifications. Meanwhile, 2.4GHz can reach up to 8,000Hz, making it an excellent choice for competitive gaming, fast typing, or coding, where split-second responsiveness is crucial. Bluetooth, however, works perfectly well for general office tasks or casual use.
Connection Stability and Range
In crowded spaces, 2.4GHz wireless excels in maintaining a stable connection. Its dedicated USB receiver establishes a private radio frequency link, reducing the likelihood of interference. Additionally, 2.4GHz protocols use adaptive frequency hopping to automatically switch channels when interference is detected, ensuring uninterrupted performance.
Bluetooth, while convenient, shares bandwidth with other nearby devices. This can lead to occasional communication delays or data drops in busy environments. Although newer Bluetooth versions (5.2 and above) have made strides in improving stability, they still trail behind 2.4GHz in terms of raw speed and reliability. The table below summarizes these differences.
Comparison Table: 2.4GHz vs. Bluetooth
| Feature | 2.4GHz Wireless | Bluetooth |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | 1–3ms | 7–20ms |
| Polling Rate | Up to 8,000Hz | Capped at 125Hz |
| Connection Type | Dedicated USB dongle | Built-in (no dongle required) |
| Stability | High (private channel + FHSS) | Moderate (shared bandwidth) |
| Multi-Device Support | Single device per dongle | Supports up to 7 devices |
| Battery Life | 3–6 months | 6–18 months |
| Best For | Gaming, coding, fast typing | Mobile work, multi-device use, travel |
If you’re someone who needs instant responsiveness, like a competitive gamer, programmer, or professional working at a dedicated desk, a 2.4GHz wireless keyboard is the way to go. On the flip side, Bluetooth keyboards shine for users who frequently travel, juggle multiple devices, or work in setups where USB ports are scarce.
Interestingly, many modern keyboards now offer tri-mode connectivity, allowing seamless switching between USB-C wired, 2.4GHz wireless, and Bluetooth modes. This flexibility ensures you can adapt to any situation, whether it’s gaming, office work, or working on the go.
Security Considerations in 2.4GHz Wireless Keyboards
Encryption Practices
Some high-end 2.4GHz keyboards implement AES encryption to secure keystrokes, offering protection against eavesdropping on sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. However, lower-end models often transmit data without encryption, leaving users exposed. Since manufacturers decide how to implement security features, there’s no guarantee of protection unless the vendor explicitly states the use of AES encryption.
Older keyboard models, such as certain Microsoft devices, have been found using weak XOR encryption based on the device's MAC address. This outdated method introduces significant vulnerabilities.
"In order to prevent eavesdropping, high-end keyboards encrypt the keystroke data before it is transmitted wirelessly to the USB dongle".
Unfortunately, inconsistent encryption practices have led to several notable security flaws, as outlined below.
Common Vulnerabilities
Inconsistent encryption standards have exposed 2.4GHz keyboards to critical vulnerabilities. In July 2016, Marc Newlin and the Bastille Research Team uncovered "KeySniffer", a vulnerability that affected keyboards from eight vendors, including HP, Anker, Kensington, and Toshiba. This flaw allowed attackers to use a $12 radio device to intercept and inject keystrokes from up to 250 feet away on devices transmitting data without encryption.
Keystroke injection attacks present an even greater risk. In February 2016, Newlin also revealed the "MouseJack" vulnerability, which enabled attackers to inject malicious commands into a victim’s computer via the USB dongle - even if the keyboard itself was encrypted. Logitech addressed this issue by releasing firmware updates to patch the flaw. These incidents highlight the need for robust encryption in 2.4GHz wireless communication.
| Vulnerability | Security Flaw | Affected Vendors (Examples) |
|---|---|---|
| KeySniffer | Lack of encryption (clear-text transmission) | Anker, HP, Kensington, Toshiba, RadioShack |
| KeyJack | Keystroke injection into encrypted dongles | AmazonBasics, Dell, Lenovo, Logitech |
| MouseJack | Unauthorized pairing and keystroke injection | Logitech, Dell, Microsoft, Lenovo |
To protect your device, ensure it uses AES encryption and regularly update its firmware. Check with your manufacturer - especially if you own a Logitech or Dell keyboard - for the latest patches. For highly sensitive environments, consider switching to a wired keyboard or a Bluetooth model that adheres to modern security standards. Additionally, unplugging the USB dongle when the keyboard is not in use can help prevent unauthorized access.
Frequency Band Management and Interference
The ISM Band and Shared Frequency Space
The 2.4GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band spans from 2,400 MHz to 2,483.5 MHz, providing 83.5 MHz of spectrum. This unlicensed frequency range is shared by a variety of devices, including Wi-Fi routers and even microwave ovens. Since it's unlicensed, every device operating in this range must handle the interference caused by others.
The situation gets trickier when Wi-Fi networks use wide channels (20–22 MHz), which overlap with the much narrower channels (about 1 MHz) used by devices like wireless keyboards. This limited number of non-overlapping channels can lead to adjacent-channel interference. Additionally, microwave ovens, which emit high-power signals around 2.45 GHz, can disrupt nearby signals within a 10-foot radius. To make matters worse, USB 3.0 ports, with their 5 Gbps data signaling, can also create radio frequency noise in the 2.4 GHz range. All of this underscores the need for effective interference management protocols.
Interference Mitigation Strategies
Wireless keyboards use a range of dynamic strategies to maintain reliable performance in this crowded frequency space. Many rely on frequency-agile protocols that monitor channel conditions and automatically switch to a clearer frequency when interference becomes too intense. Others use collision avoidance algorithms, which ensure data transmission only occurs when the channel is clear.
Proper hardware placement is another simple yet effective way to reduce interference. For example, using a USB extension cable to position the keyboard's dongle away from your computer's internal components can help, as signal strength decreases significantly with distance. Placing the receiver at least 3–6 feet from Wi-Fi routers and keeping it 10 feet away from microwave ovens can also make a noticeable difference.
"The #1 fix: Move your devices to 5 GHz Wi-Fi. It eliminates most interference instantly because it uses a completely different frequency." – S3Semi
For those tweaking router settings, switching your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi to channels 1, 6, or 11 can minimize interference. Additionally, moving high-bandwidth devices to the 5GHz or 6GHz bands can free up space in the 2.4GHz band. If you're using 40 MHz bandwidth, reducing it to 20 MHz can also help prevent sideband distortion, which can overwhelm low-power devices like wireless keyboards.
Choosing the Right 2.4GHz Wireless Keyboard
Key Factors to Consider
When selecting a 2.4GHz wireless keyboard, it's essential to strike a balance between performance and practicality, especially if you’re tailoring your choice for specific uses like gaming or productivity.
For gaming, low latency and high polling rates are crucial. A 2.4GHz keyboard typically achieves latency as low as 1–2ms, with polling rates reaching up to 8,000Hz. In contrast, Bluetooth keyboards are limited to a 125Hz polling rate and latency of 5–20ms, making them less ideal for fast-paced gaming sessions.
However, high polling rates come at a cost - battery life. For example, using an 8,000Hz polling rate on a 500mAh battery may only last 12–15 hours, while a 1,000Hz setup can stretch to 70–80 hours. Add RGB lighting into the mix, and battery runtime decreases even further.
When it comes to layout, full-size keyboards are a great choice for productivity, while smaller layouts like 60%, 65%, or 75% mechanical keyboard kits are better for portability. Tri-mode connectivity keyboards, which support USB-C, 2.4GHz wireless, and Bluetooth, offer added versatility for switching between devices.
For the best performance, consider the placement of your wireless dongle. Positioning it 12–20 inches from the keyboard and avoiding rear I/O ports near metal cases can significantly reduce packet loss - by as much as 30–50% in crowded wireless environments.
By aligning your choice with these considerations, you can ensure your keyboard meets both your performance demands and daily usability needs.
Examples from KeebsForAll
KeebsForAll offers several models that incorporate these essential features. The Neo70 (starting at $164.00) and Neo80 (starting at $189.00) boast tri-mode connectivity, CNC aluminum cases, and hot-swappable PCBs. These options are great for users who value flexibility and durability.
For those seeking a more premium build, the Freebird75 Full Kit (starting at $199.00) and Freebird TKL Full Kit (starting at $249.99) provide multiple mounting styles and support for various layouts, catering to a more customizable experience.
Gamers might be drawn to the MonsGeek M1W-SP HE, available fully assembled for $159.99. This keyboard features magnetic switches with TMR sensors for lightning-fast actuation, making it an excellent pairing with the low-latency 2.4GHz connection. Additionally, all these models support hot-swapping, allowing users to experiment with different switches - linear switches for gaming or tactile ones for typing.
These options from KeebsForAll ensure that you can find a keyboard tailored to your specific needs, whether you prioritize speed, durability, or customization.
Conclusion
Understanding how 2.4GHz protocols work can help you pick a keyboard that suits your workflow. These keyboards are known for their quick responsiveness, making them ideal for gaming and other demanding tasks.
One of the standout features of 2.4GHz keyboards is their true plug-and-play convenience. Unlike Bluetooth, they skip the hassle of pairing, offering a smoother setup experience. This simplicity translates into noticeable performance benefits in everyday use.
To ensure stable performance, keep the USB receiver away from sources of interference like USB 3.0 cables or microwave ovens. Additionally, features like adaptive frequency hopping allow 2.4GHz keyboards to maintain a reliable connection, even in environments crowded with Wi-Fi routers and other devices.
For those who need flexibility, tri-mode keyboards are a great option. They combine the high-speed performance of 2.4GHz for intensive tasks with the convenience of Bluetooth for mobile devices. This dual capability lets you switch between scenarios without sacrificing responsiveness where it matters most.
FAQs
Will 2.4GHz wireless work on phones and tablets?
Yes, devices using 2.4GHz wireless protocols can connect seamlessly with phones and tablets. This frequency range is commonly utilized for wireless peripherals like keyboards and other accessories that rely on RF signals to operate.
Can I use one 2.4GHz dongle with multiple keyboards?
Yes, but this depends on whether the keyboard supports multi-device pairing. Most keyboards are designed to work with their own specific dongle or receiver. To find out, review your keyboard's specifications to see if it includes multi-device pairing capabilities.
How can I tell if my 2.4GHz keyboard is encrypted?
To find out if your 2.4GHz keyboard is encrypted, check whether it uses any encryption protocols. Generally, higher-end keyboards secure your keystrokes, while many budget options might skip encryption, making them susceptible to data interception. You can usually find this information in the keyboard's documentation or technical specifications.



![[Pre-Order] Autumn Leaves PBT Keycaps - KeebsForAll](http://keebsforall.com/cdn/shop/products/DSC09732.jpg?v=1676148273)






Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.